
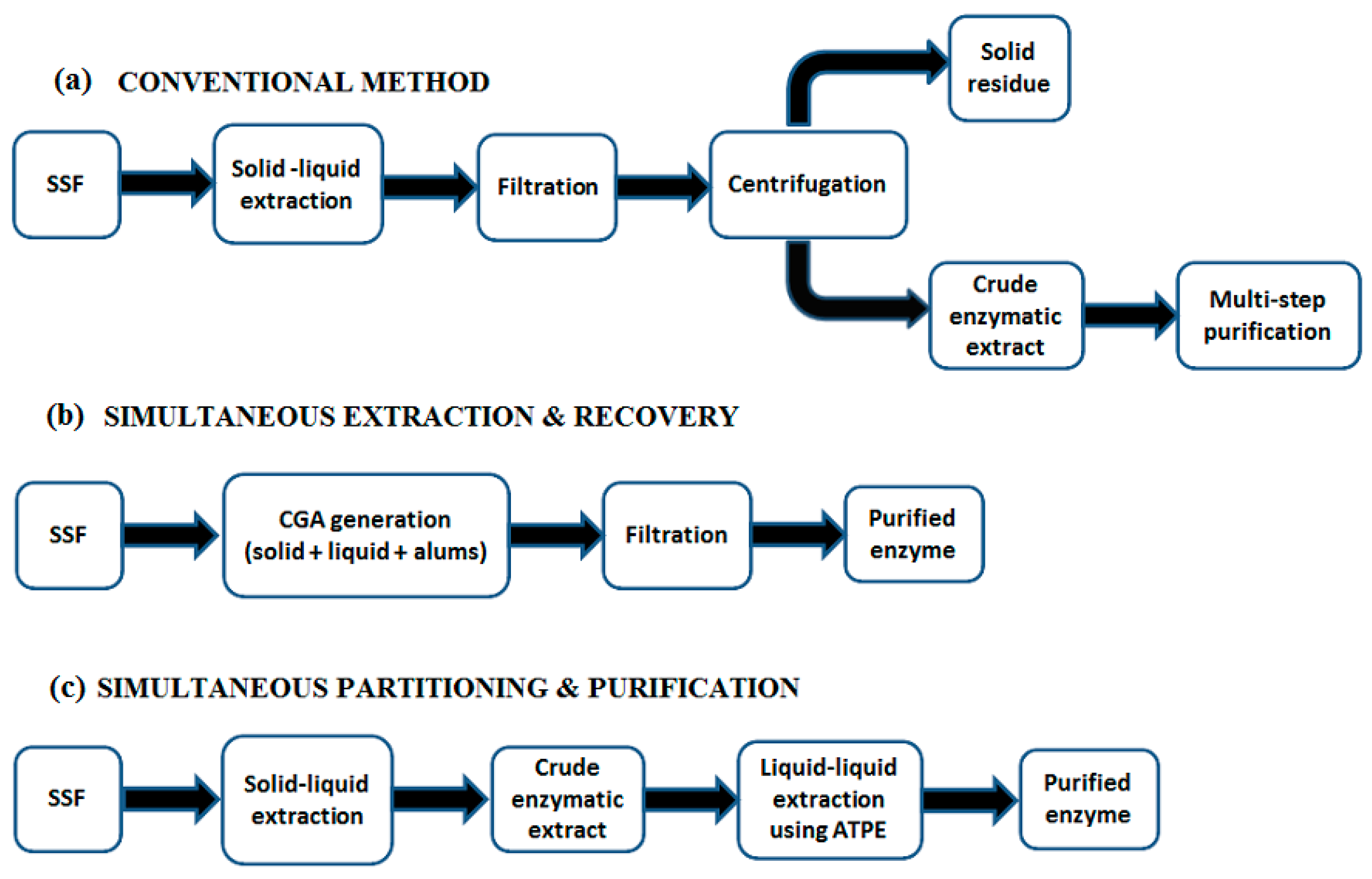
In each case, the extraction column was sized via pilot plant testing. This article presents three case studies involving the design of complete LLE systems with downstream distillation. However, in some cases, phenomena such as foaming and unknown interactions between various components in the system require pilot plant testing of downstream distillation steps to provide a firm basis for the commercial process design. Use of conventional organic solvents in an extraction brings problems such as toxicity, volatility, flammability and denaturization of biomolecules. Often, the distillation columns can be designed by first simulating the process and then designing the distillation column internals using known design criteria, hydraulic rating software, and process engineering experience. If the solvent has some solubility in the feed - as is often the case for systems that include an aqueous feed and an organic solvent - then a distillation column will be required to recover and recycle the solvent from the aqueous phase (raffinate).Īs discussed in previous articles (1–2), design of the extraction column almost always requires pilot plant testing to provide data for accurate scale-up and design of the commercial column. Other purification techniques such as membrane separation, liquid-liquid extraction, distillation. Typically, the solvent used for the extraction step must be distilled from the extracted solute and then recycled back to the extraction column. Currently, the evaporation process is being investigated. Thus, optimizing the process requires the engineer to focus on the overall integration of the extraction and distillation columns. Contents: Introduction and course contents - Bioprocess case studies/flow sheet - Characteristics of biomolecules and their differences - Various down stream process steps - Fundamental principles of obtaining the product from cell cultures intracellular vs. In most chemical separation applications involving liquid-liquid extraction (LLE), the process will require one or more distillation columns downstream of the extraction column. This article describes the process design of such systems. Currently various intensification techniques are being applied in the field of liquid-liquid extraction for improving the process efficiency like hybrid processes, reactive extraction, use of ionic liquids etc, which are gaining importance due to the cost associated with the downstream processing of the fermentation products (20-50% of total production cost).Liquid-liquid extraction processes often require one or more downstream distillation columns. The principles, types, equipment and applications of liquid-liquid extraction for bioproducts are discussed. Liquid-liquid extraction process is particularly suitable for biorefinery process (through conversion using microorganisms), featuring mild operational conditions and ease of control of process. With the availability of variety of solvents as well as commercial equipment, liquid-liquid extractions finds applications in fields like chemicals and bio-products, food, polymer, pharmaceutical industry etc. Solvent extraction one of the oldest approaches of separation known, remains one of the most well-known methods operating on an industrial scale.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
